Recreational vehicles (RVs) are designed for comfort, convenience, and efficiency while on the road. Whether you are traveling long distances, camping in remote locations, or simply enjoying a weekend getaway, having a reliable power supply is crucial to ensuring a hassle-free experience. One crucial component that plays a significant role in ensuring a smooth and seamless experience is the RV power supply dual voltage interface. This system allows RVs to operate efficiently by managing power distribution and ensuring that appliances receive the correct voltage needed to function properly. Without a well-functioning dual voltage interface, RV owners may experience electrical issues, reduced battery life, or even appliance failures. Understanding how this system works, its importance, and how to maintain it is essential for any RV owner looking to optimize their vehicle’s performance and extend the longevity of their electrical components.
In this article, we will dive into the details of an RV power supply dual voltage interface, explaining its functionality, benefits, and maintenance, along with some troubleshooting tips.
Understanding RV Power Systems
Before we explore the dual voltage interface, let’s first understand how an RV power system works. RVs require electricity to operate essential appliances such as lights, refrigerators, heating systems, air conditioners, and entertainment units. This electricity can come from two main sources:
- Shore Power – When the RV is plugged into an external power source (campground hookup, generator, etc.).
- Battery Power – When using the RV’s onboard batteries, which store energy and power essential systems when external power is unavailable.
These power sources deliver electricity at different voltages, and this is where the dual voltage interface comes into play.
What is a Dual Voltage Interface in an RV Power Supply?
A dual voltage interface in an RV power supply is a system that manages and distributes power at two different voltage levels—typically 120V AC (alternating current) and 12V DC (direct current). This dual voltage capability is necessary because different RV appliances and systems require different types of electrical power.
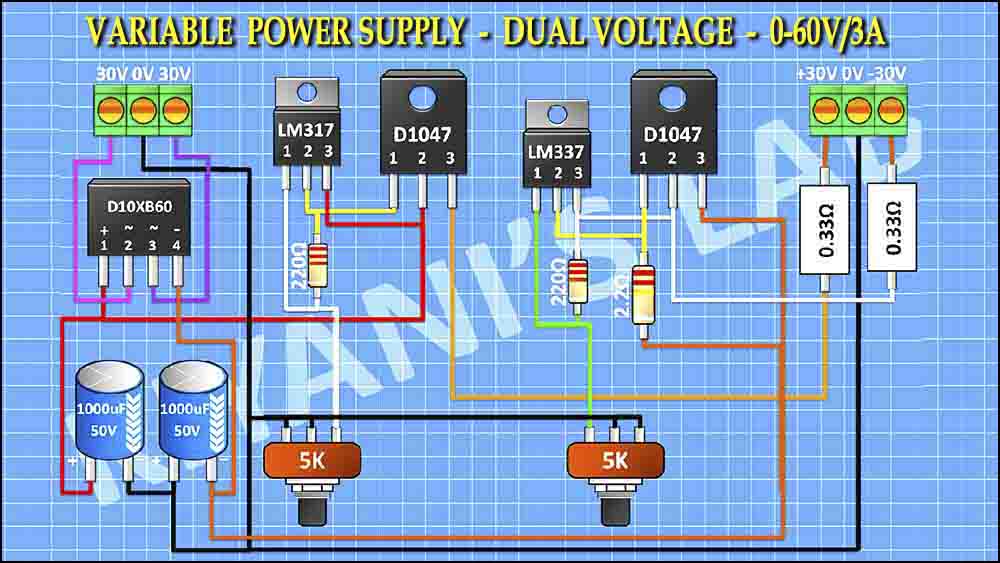
- 120V AC Power – Used for high-energy appliances like air conditioners, microwaves, TVs, and refrigerators when plugged into shore power.
- 12V DC Power – Powers essential systems like lighting, water pumps, fans, and electronic control panels using the RV’s battery system.
The power converter or inverter ensures that both voltage levels are properly managed so that your RV functions efficiently in any situation.
Components of an RV Dual Voltage System
1. Power Converter
- Converts 120V AC power to 12V DC power to run essential DC-powered appliances.
- Charges the RV’s battery when connected to shore power.
2. Inverter
- Converts 12V DC power back to 120V AC to run appliances when shore power is not available.
- Allows for limited use of high-energy appliances through battery power.
3. Battery Bank
- Stores 12V DC power to be used when shore power is unavailable.
- Powers essential systems and appliances that rely on DC power.
4. Shore Power Connection
- Provides 120V AC power from an external source.
- Directly powers AC appliances and allows the power converter to charge the batteries.
5. Distribution Panel
- Distributes power to various circuits in the RV.
- Contains fuses and breakers for safety and overload protection.
How Does the Dual Voltage Interface Work?
When you plug your RV into shore power, the power converter steps in to convert 120V AC into 12V DC, ensuring that both voltage systems work together seamlessly. This allows:
- AC appliances to run directly from shore power.
- The converter to charge the batteries while simultaneously providing 12V DC to appliances that need it.
When shore power is unavailable, the battery system provides 12V DC power to essential appliances. If an inverter is installed, it can convert 12V DC to 120V AC for limited use of high-power devices.
Benefits of a Dual Voltage Interface in RVs
- Efficient Power Distribution – Ensures all appliances receive the correct type of power for optimal operation.
- Battery Management – Keeps the RV battery charged while plugged into shore power.
- Flexibility – Allows RV owners to use both AC and DC-powered devices without manual switching.
- Energy Savings – Reduces reliance on generators and enhances battery efficiency.
- Backup Power – Provides an alternative power source in case of electrical failures or unavailability of shore power.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Like any electrical system, an RV power supply dual voltage interface may face some issues. Here are common problems and how to troubleshoot them:
Battery Not Charging
- Possible Causes: Faulty power converter, blown fuse, or poor wiring connection.
- Solution: Check the power converter, inspect fuses, and ensure all connections are secure.
No Power to AC Appliances

- Possible Causes: Tripped circuit breaker, disconnected shore power, or faulty inverter.
- Solution: Reset circuit breakers, check shore power connection, and inspect the inverter.
Dim or Flickering Lights
- Possible Causes: Weak battery, loose wiring, or a failing power converter.
- Solution: Test battery voltage, tighten loose wires, and check the power converter functionality.
Overheating of Converter or Inverter
- Possible Causes: Overloading, poor ventilation, or internal failure.
- Solution: Reduce power usage, ensure proper ventilation, and consider replacing the unit if necessary.
Maintenance Tips for RV Power Supply Dual Voltage Interface
To keep your RV’s power supply working efficiently, follow these maintenance tips:
- Regularly Check Battery Levels – Keep batteries charged and replace old ones when necessary.
- Inspect and Clean Electrical Connections – Prevent corrosion and loose connections.
- Monitor Power Converter and Inverter Performance – Ensure they are functioning correctly and replace them if needed.
- Check Circuit Breakers and Fuses – Replace blown fuses and reset tripped breakers.
- Ensure Proper Ventilation for Power Components – Avoid overheating by maintaining good airflow.
- Understand Power Draw – Make sure you are aware of how much power your appliances consume to prevent overloading the system.
- Use Surge Protectors – Protect your electrical system from voltage spikes by investing in quality surge protectors.
- Upgrade to Lithium Batteries – If possible, switch to lithium-ion batteries for better efficiency and longer lifespan.
- Have a Backup Generator – Carrying a backup generator can be a lifesaver when dealing with power shortages.
- Regular Professional Inspections – Have an RV electrical technician inspect your system periodically to ensure everything is in good condition.
By following these maintenance and troubleshooting steps, you can ensure a reliable and efficient power supply for your RV, making your road trips stress-free and enjoyable. A well-maintained dual voltage interface system can extend the lifespan of your electrical components and enhance your overall RV experience.
Read More: How the Jaguar S-Type R Oil Cooler Works